
Starlab LLC
The Starlab commercial space station will launch on SpaceX’s Starship rocket, officials said this week.
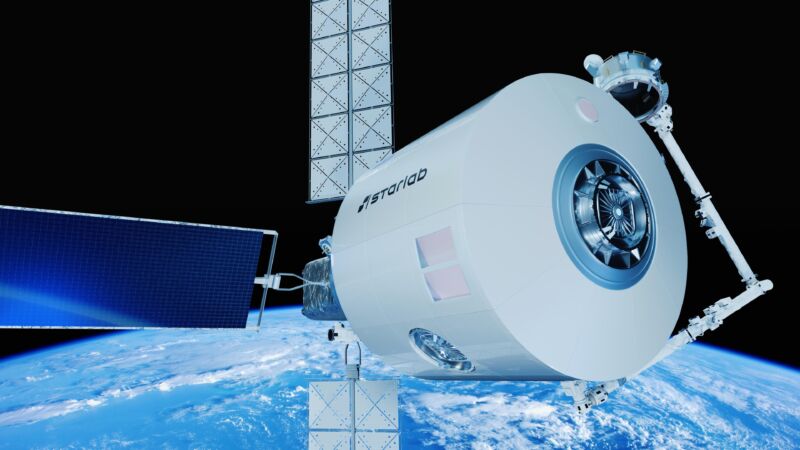
Starlab is a joint venture between the US-based Voyager Space and the European-based multinational aerospace corporation Airbus. The venture is building a large station with a habitable volume equivalent to half the pressurized volume of the International Space Station and will launch the new station no earlier than 2028.
“SpaceX’s history of success and reliability led our team to select Starship to orbit Starlab,” Dylan Taylor, chairman and CEO of Voyager Space, said in a statement. “SpaceX is the unmatched leader for high-cadence launches and we are proud Starlab will be launched to orbit in a single flight by Starship.”
Fitting in a big fairing
Starlab will have a diameter of about 26 feet (8 meters). It is perhaps not a coincidence that Starship’s payload bay can accommodate vehicles up to 26 feet across in its capacious fairing. However, in an interview, Marshall Smith, the chief technology officer of Voyager Space, said the company looked at a couple of launch options.
“We looked at multiple launches to get Starlab into orbit, and eventually gravitated toward single launch options,” he said. “It saves a lot of the cost of development. It saves a lot of the cost of integration. We can get it all built and checked out on the ground, and tested and launch it with payloads and other systems. One of the many lessons we learned from the International Space Station is that building and integrating in space is very expensive.”
With a single launch on a Starship, the Starlab module should be ready for human habitation almost immediately, Smith said.
Starlab LLC
Starlab is one of several privately developed space stations vying to become a commercial replacement for the International Space Station, which NASA is likely to retire in 2030. Among the other contenders are Axiom Space, Blue Origin, and Vast Space. SpaceX may also configure a human-rated version of Starship as a temporary space station.
NASA has provided seed funding to some of these companies, including Voyager Space, to begin designing and developing their stations. NASA is expected to hold a second round of competition next year, when it will select one or more companies to proceed with building and testing their stations.
Finding customers
Each company is developing a space station that will serve both government customers—NASA wants to continue flying at least a handful of astronauts in low-Earth orbit for research purposes—as well as private customers. The challenge for Starlab and other commercial stations is developing a customer base beyond NASA to support the expense of flying and operating stations.
The challenge is a huge one: NASA spent more than $100 billion constructing the International Space Station and has a $3 billion annual budget for operations and transportation of people and supplies to the station. The agency is likely to fund commercial space stations at a level of about $1 billion a year, so these companies must build their facilities relatively quickly at low cost and then find a diverse base of customers to offset expenses.
Starlab may have an advantage in this regard with its co-ownership by Airbus. One of the big questions surrounding the end of the International Space Station is what happens to the European astronauts who fly there now. The European Space Agency will likely be reticent about funding missions to private space stations owned and operated by US companies. The involvement by Airbus, therefore, makes Starlab attractive to European nations as a destination.
